Progress till Midterm Evaluation @RTEMS-GSoC-2025
Milestones Achieved
The period in GSoC until now has been pretty thrilling and rewarding. During this time till Midterm Evaluation of GSoC 2025 @RTEMS Project, I accomplished the following milestones :
- GRETH lwIP Driver successfully being Initialized and this is tested
- Code for GRETH Transmission Mechanism and handling of Transmission related Interrupts ready
- Progress in testing GRETH lwIP Driver
- GRETH Legacy Driver successfully simulated and tested
- FLowchart for the tests used, across RTEMS networking packages
- Notes made while studying GRETH Legacy Driver and TMS570 lwIP driver
Project overview
GRETH is an Ethernet Media Access Controller from Frontgrade Gaisler. Currently, support for this driver in RTEMS exists only for the Legacy Networking Stack. However, lwIP, which stands for lightweight Internet Protocol is a newly emerging network stack, which is getting popular, owing to its compatibility with embedded systems, its lower memory footprint and simpler logic, among its other benefits. This project aims to provide GRETH Network driver for RTEMS lwIP Network Stack, for the LEON3 processor, which is based on SPARC Architecture
Progress In Detail…
- GRETH lwIP Driver successfully being Initialized and this is tested :
- Before this project, RTEMS lwIP Package did not have support for GRETH as well as for
sparc/leon3BSP. My first milestone for my GSoC project was to provide support forsparc/leon3BSP by starting to write GRETH Driver for RTEMS lwIP Networking Stack, thus building this package for the first time for GRETH as well assparc/leon3BSP. I feel very happy to tell that with the new code for RTEMS lwIP GRETH Driver, and after days of debugging and fixing warnings and errors, the lwIP Networking Stack now builds successfully, without even any warnings!
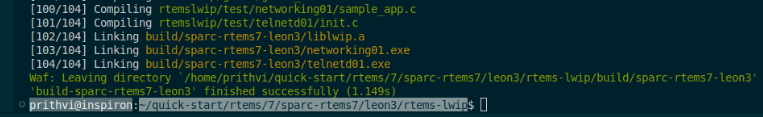
- The commit ID at which the successful build was first noted is (clickable link):
0680fb98e91d2f418daedb54964782dfa6c8f6eeon branchPrithvi-GSoC-25 - The initialization of the GRETH lwIP Driver has been tested using
printf()statements at various phases in the driver code, and usingtelnetd01.exeapplication from RTEMS lwIP itself, being run in SIS.
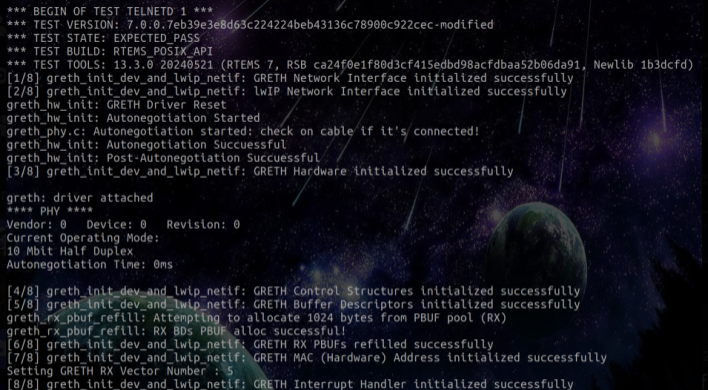
- Before this project, RTEMS lwIP Package did not have support for GRETH as well as for
- Code for GRETH Transmission Mechanism and handling of Transmission related Interrupts ready :
- The code for GRETH lwIP driver transmission mechanism, along with required interrupt handling for transmission mechanism, is ready. The code is written keeing in mind the working as studied from GRETH Legacy Driver, in RTEMS Legacy Networking, and various learnings from TMS570 Ethernet Driver in RTEMS lwIP.
- The commit ID at which the successful build with the whole transmission mechanism was first noted is (clickable link):
337b7f570fd02a3618dfe0f6d3df316ebbc042d4on branchPrithvi-GSoC-25
- Progress in testing GRETH lwIP Driver :
- Immediately after having code for transmission mechansim ready, I worked on testing this mechanism.
- To verify the transmission of GRETH lwIP Driver, I decided to use Wireshark, to check packet transmission from the driver.
- The approach I used was to create a Shell having a command registered for a transmission test of GRETH lwIP driver, and run it and then check the packets transmitted on Wireshark. Here, I decided to go with Unicast transmission, transmitting UDP packets from GRETH lwIP driver configured with a specific IP address, to another IP address on the same network. The test for this is
udp_test.exe. I worked on this test on branch Prithvi-GSoC-25-Tests - However on running the driver, at the Commit Hash , I wasn’t getting tap interface created and attached to lxcbr0 bridge, which I checked using
brctl show, which shown no interfaces attached to lxcbr0 bridge. According to sis.pdf documentation, this meant that the GRETH core isn’t initialized by my test application. - I also noticed there isn’t any driver function for GRETH Driver in RTEMS lwIP like rtems_leon_greth_driver_attach() in RTEMS Legacy Neteowrking Package, for getting base address of GRETH Driver and resetting the driver. After that, the task of driver attach was performed using analogous lwIP function
netif_add(). So I immediately started working on adding such a function for lwIP and declaring prototype of this new function atINSTALL_PREFXI/sparc-rtems7/leon3/lib/include/bsp.hwhich corresponds tobsp.hfile which I installed for my BSP (sparc/leon3here). - In RTEMS Legacy Networking, the test I used,
telnetd02.exe, usesstruct rtems_bsdnet_iconfigto initialize tye GRETH Interface and the driver attach function used there was
#ifndef RTEMS_BSP_NETWORK_DRIVER_NAME
#define RTEMS_BSP_NETWORK_DRIVER_NAME RTEMS_BSP_NETWORK_DRIVER_NAME_GRETH
#define RTEMS_BSP_NETWORK_DRIVER_ATTACH RTEMS_BSP_NETWORK_DRIVER_ATTACH_GRETH
#endif
and we also have :
#define RTEMS_BSP_NETWORK_DRIVER_ATTACH_GRETH rtems_leon_greth_driver_attach,
all defined in the same file :INSTALL_PREFXI/sparc-rtems7/leon3/lib/include/bsp.h. This is where I thought to implement a similar function for lwIP :
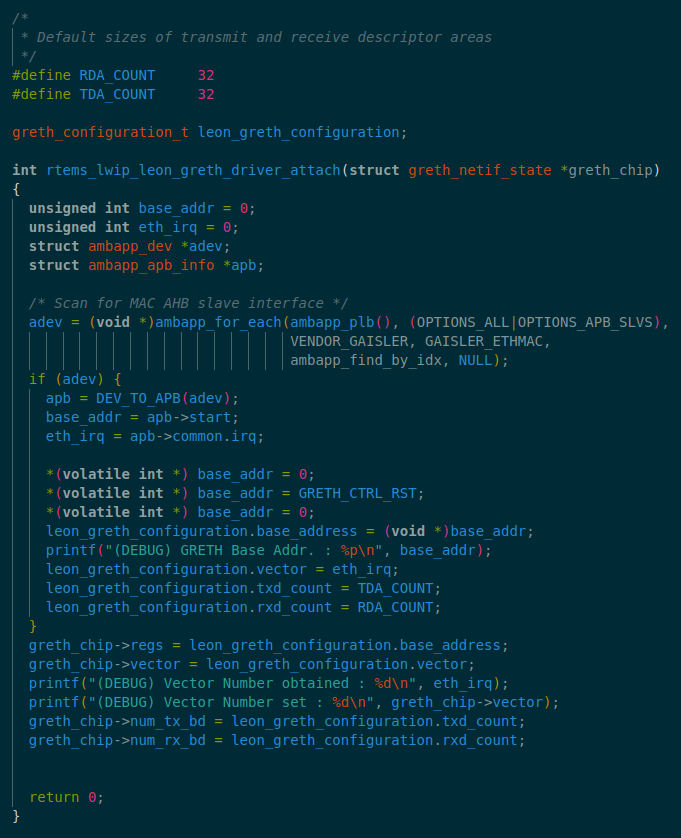
- I also inlcuded the function prototype at RTEMS source repository’s
rtems/bsps/sparc/leon3/include/bsp.hfile with
#ifdef RTEMS_NETWORKING
#include "greth_emac.h"
#endif
for conditional compilation ofgreth_emac.hwhen RTEMS Networking Stack is up during the compilation process. This resolved th errors ofgreth_emac.hmissing in spite of being installed, during initial stage of RTEMS build, when the networking functionslaities weren’t available. - Continuing further, the GRETH Driver showed improvement as follows :
- The vendor ID and device ID were now configured and prinetd successsfully in SIS terminal, resolving any issues of wrong pointer being used.
- Generally, the folllowing line shows up when an application enables GRETH core successfully in the sense that
tap0interface is created automatically which attaches itself tolxcbr0bridge. The following image showstelnetd02.exetest from RTEMS Legacy Networking Package being run with GRETH lwIP driver, as confirmed from the(DEBUG) GRETH Base Addr. : 0x80000b00line, which is a debug satatement which I have added only to lwIP specificrtems_lwip_leon_greth_driver_attach()function. The vendor ID and dvice ID are as obtained withudp_test.exetest. On successful configuraton of GRETH by this legacy networking application, the used MAC address and tap interface are printed.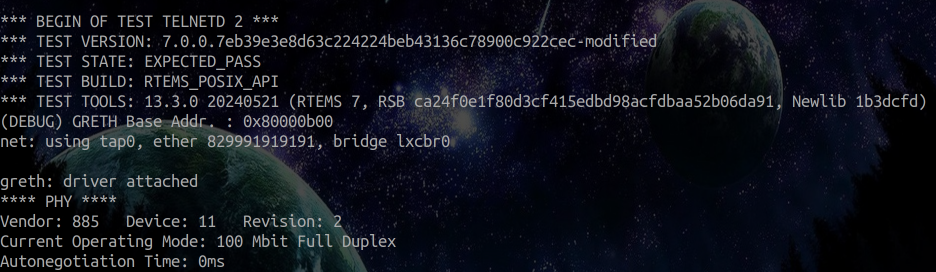
- However, right now, I am just getting
net: hwaddr error. Though this is an error, I am confident to resolve it, delving further into GRETH configuration and initialization and its connection with lwIP.
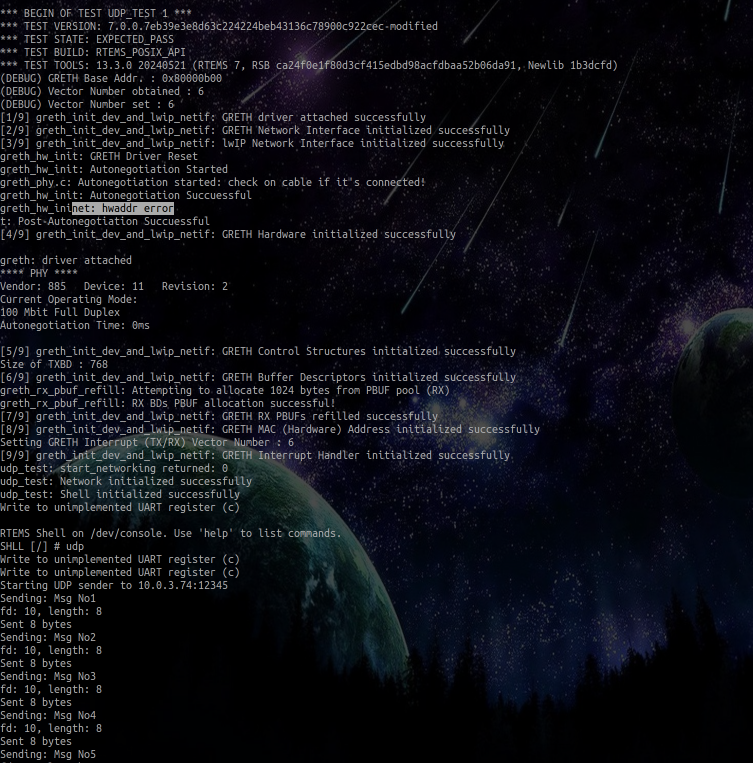
- Here is the test at commit
2e8cb5dcb3dadfb49c67e2b51d430b6b3b07877con my fork of RTEMS lwIP (branch Prithvi-GSoC-25-Tests) which I have created until now. The test works fine, it transmits UDP packets at regular intervals. However, I am just facing few issues in tracking the reception of these packets, due to error in tap interface creation and am working actively to resolve them.
- However, right now, I am just getting
- GRETH Legacy Driver successfully simulated and tested :
- A key aspect of this project was to simulate GRETH Legacy Driver. For this milestone, I had encountered several problems, like memory alignment issues, connectivity issues, etc. due to which I wasn’t able to simulatye the working of GRETH Legacy Driver. However, it was due to all these errors that I got the opportunity to dive deep into RTEMS codebase, so as to work on these issues in a better way. I learnt about the importance and method of configuration of struct
rtems_bsdnet_configandrtems_bsdnet_ifconfig, working withsparc-rtems7-gdb, using tools likeaddr2line,sparc-rtems7-objdump, etc. to name a few important learnings. - Finally, referring to RTEMS Networking Tests I tried making a unicast client, which sends a message to an IP address (GRETH LEgacy Driver IP Address)
This was verified by monitoring the UDP Packets received by Legacy GRETH Driver usingtcpdumputility.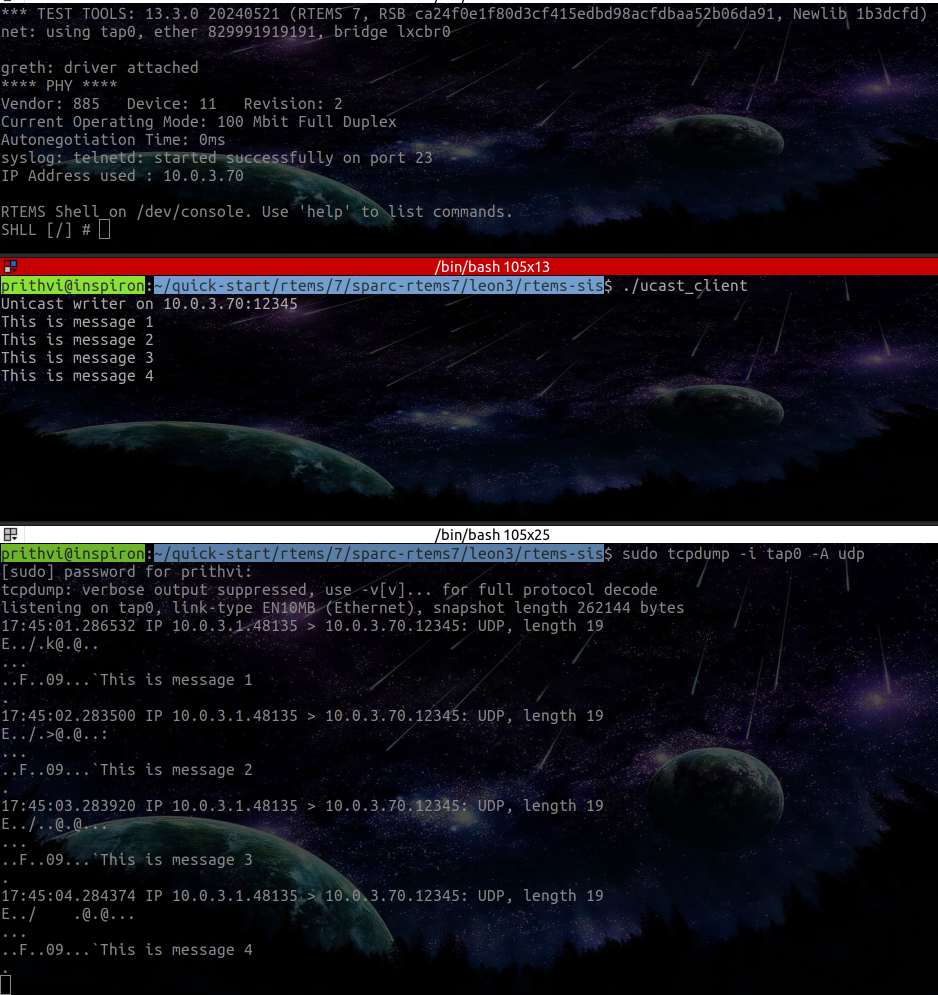
telnetd02.exeapplication from RTEMS LEgacy Networking, has a commandnetstatsusing which, dteailed statistics regading the recent communication session, could be obtained. The statistics for the above result shown proper statistics.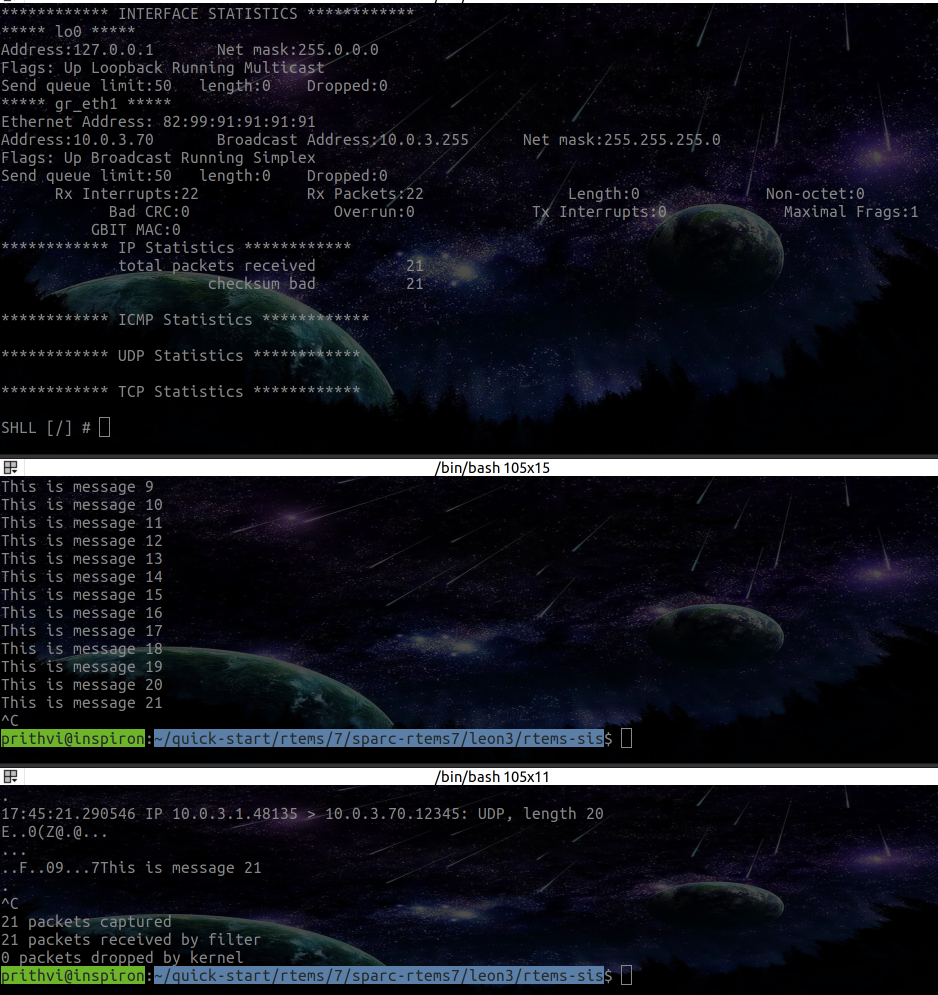 Further, using
Further, using netcastI was also able to transmit custom UDP packets to the Legacy GRETH Driver and it shown proper reception.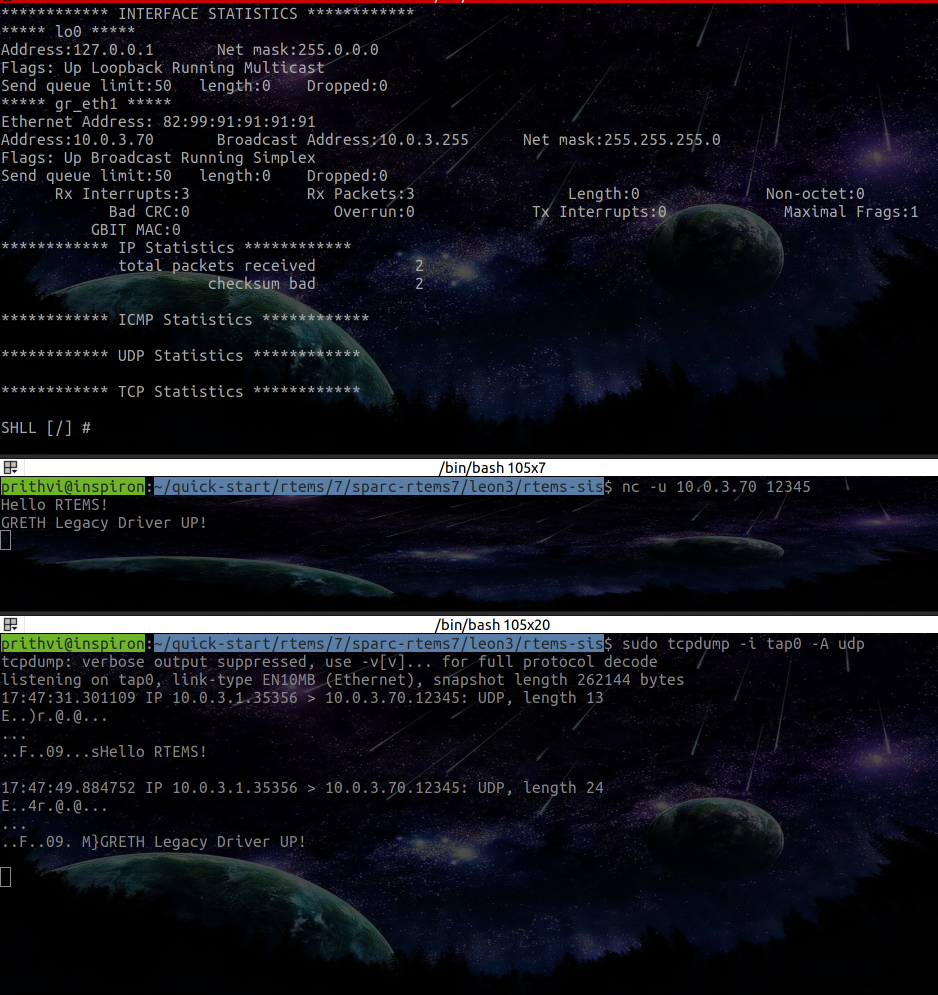 After checking that my unicast UDP client test works, I pushed it to my branch of my fork of RTEMS Networking Tests
After checking that my unicast UDP client test works, I pushed it to my branch of my fork of RTEMS Networking Tests
- A key aspect of this project was to simulate GRETH Legacy Driver. For this milestone, I had encountered several problems, like memory alignment issues, connectivity issues, etc. due to which I wasn’t able to simulatye the working of GRETH Legacy Driver. However, it was due to all these errors that I got the opportunity to dive deep into RTEMS codebase, so as to work on these issues in a better way. I learnt about the importance and method of configuration of struct
-
Work with tests across RTEMS networking packages : I worked with several tests from RTEMS Legacy Networking, Legacy Networking Demos, Net Services and lwIP. Here is a flowchart summarizing my progress while using them.
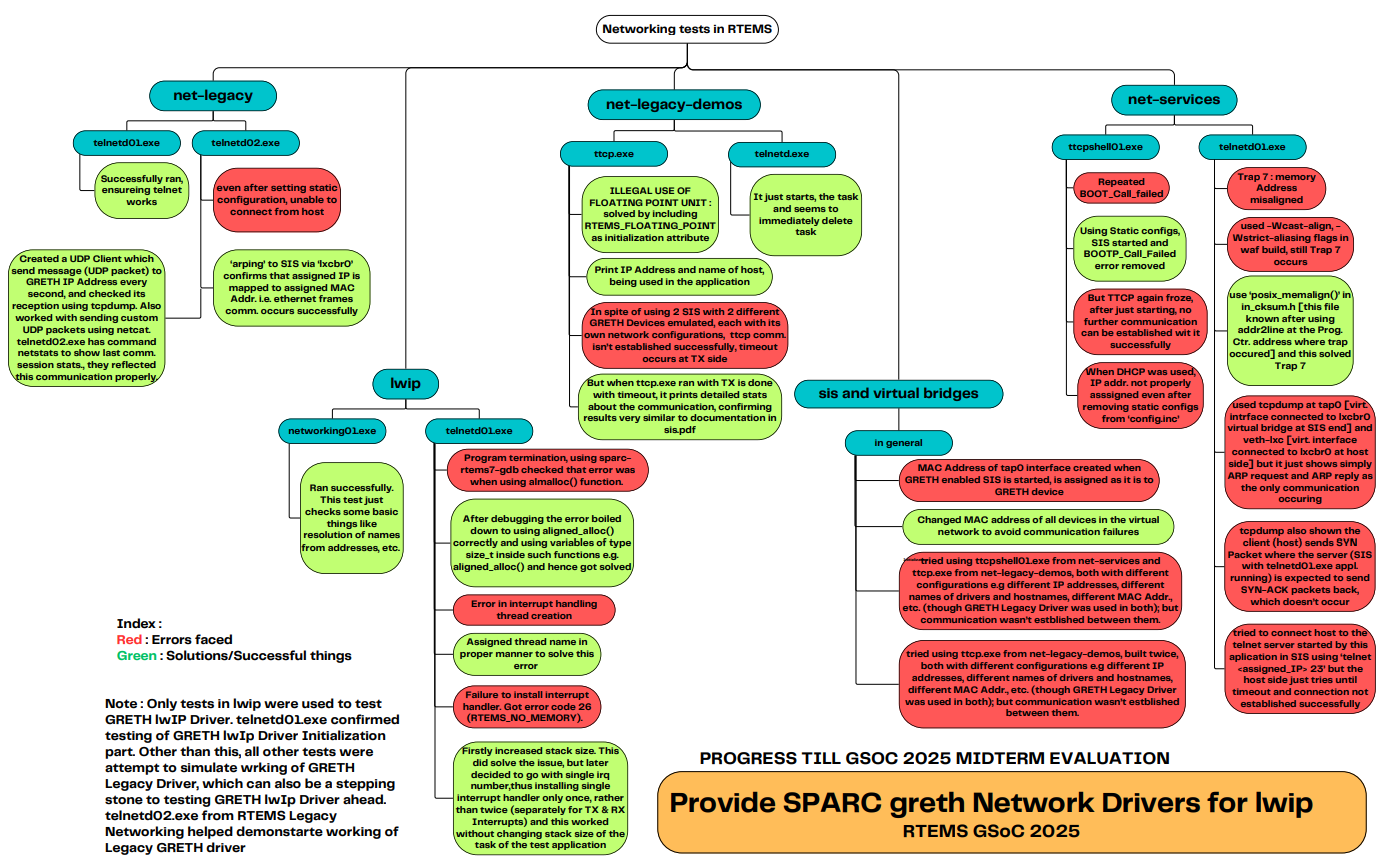
- Notes made while studying GRETH Legacy Driver and TMS570 lwIP driver : In the initial phasse of coding period, I began with studying GRETH Legacy Driver for GRETH driver intricacies and TMS570 Ethernet Driver for lwiP intricacies. At that time, I made doxygen comments as my notes for these drivers on my forks. Here are their links :
Problems faced (an overview)
Over this whole period till now, I faecd a lot of problems. These were the stepping stones towards my new learnings in this journey. Here are few of the errors I faced in this phase till Midterm evaluation :
-
BOOTP_call_failederror while simulating Legacy GRETH Driver. This was due to BOOTP mechanism not working and hence, GRETH driver not getting an address assigned. This was when I first started this simulation, using default (BOOTP) network configuration. -
Memory Address not aligned a.k.a.
trap 7error in SIS : SPARC processors like LEON3 require memory addresses to be 4 byet aligned. When this rule is not followed, such exception occurs. This was solved by using methods likealigned_alloc(),__aligned(), etc. -
Error codes like
26fromrtems_interrupt_handle_install()which meansRTEMS_NO_MEMORYdue to memory constraints
Methods and Steps used for simulation
These tests have been tested on Ubuntu 22.04.5 LTS (jammy)
- Installing RTEMS : Follow these steps to install RTEMS. Here, the installation prefix chosen is
$HOME/quick-start/rtems/7.- Clone the repositories to obtain the sources
>>> mkdir -p $HOME/quick-start/src>>> cd $HOME/quick-start/src>>> git clone https://gitlab.rtems.org/rtems/tools/rtems-source-builder.git rsb>>> git clone https://gitlab.rtems.org/rtems/rtos/rtems.git - Installing the Tool Suite :
>>> cd $HOME/quick-start/src/rsb/rtems>>> ../source-builder/sb-set-builder --prefix=$HOME/quick-start/rtems/7 7/rtems-sparc - Build the Board Support Package, for this GSoC project, BSP is
sparc/leon3
>>> cd $HOME/quick-start/src/rsb/rtems
>>> ../source-builder/sb-set-builder --prefix=$HOME/quick-start/rtems/7 \
--target=sparc-rtems7 --with-rtems-bsp=sparc/erc32 --with-rtems-tests=yes 7/rtems-kernel - With this, we have built RTEMS and also our required BSP!
- Clone the repositories to obtain the sources
-
To create virtual bridge
lxcbr0:
lxcbr0is a virtual bridge. When an application, which uses GRETH, is runnning in SIS, a tap device is automatically created when the application enables the GRETH core. The tap can optionally be connected to a host bridge using -bridge br0 or similar at invocation. Networking requires SIS to be run as root or withsudo. To create this bridge :- Install
lxcpackage :
>>> sudo apt install lxc - Set the following configurations in file
/etc/default/lxc-net:
USE_LXC_BRIDGE="true"
LXC_BRIDGE="lxcbr0"
LXC_ADDR="10.0.3.1"
LXC_NETMASK="255.255.255.0"
LXC_NETWORK="10.0.3.0/24"
LXC_DHCP_RANGE="10.0.3.2,10.0.3.254"
LXC_DHCP_MAX="253"
LXC_DHCP_CONFILE=""
LXC_DOMAIN="lxc"using the command :
>>> sudo nano /etc/default/lxc-net - Now run the following command to start the virtual bridge
lxcbr0:
>>> sudo systemctl start lxc-net - To stop the bridge
lxcbr0use the following command :
>>> sudo systemctl stop lxc-net
- Install
-
Starting the SIS terminal :
- Clone the GitLab repository for RTEMS-SIS :
>>> git clone https://gitlab.rtems.org/rtems/tools/rtems-sis - Move to
rtems-sisdirectory
>>> cd rtems-sis - SIS uses
makebuild system. Run the following command to build SIS
>>> ./configure
>>> make - (optional) Further, to generate doccumentation for SIS, to generate a file
sis.pdf, run :
>>> make sis.pdf - Now you will be having an executable file :
sis. To start it, run (-voption enables higher verbosity; it is an optional flag) :
>>> sudo ./sis -v -leon3 -bridge lxcbr0 ./<application-file-name> - To run your application, use the command in SIS terminal:
>>> run - The application should start running
- Clone the GitLab repository for RTEMS-SIS :
-
To build RTEMS packages like : Legacy Networking, lwIP or Net Services, follow these steps :
- Clone the GitLab repository :
>>> git clone <repository-link-http-type> - Move inside the cloned repository :
>>> cd <cloned-repository> - First, populate the git submodules :
>>> git submodule init
>>> git submodule update - All these packages use
wafbuild system. So, toi use this build system, follow these steps :- Confgure the workspace. Here,
INSTALL_PREFIXis the path where RTEMS is installed :
>>>./waf configure --prefix=INSTALL_PREFIX --rtems-bsps sparc/leon3 - Build the package :
>>> ./waf build - Install the package :
>>> ./waf install
- Confgure the workspace. Here,
For Legacy Networking Demos, this process is a bit different since it uses
makebuild system. To build it, follow these steps :- Clone the GitLab repository :
>>> git clone <repository-link-http-type> - Move inside the cloned repository :
>>> cd <cloned-repository> - Set variables (for
rtems-installation-prefixcheck previous part) :
>>> export RTEMS_MAKEFILE_PATH=<rtems-install-prefix>/sparc-rtems7/leon3
>>> export PROJECT_ROOT=<rtems-install-prefix> - Then build the package :
>>> make
- Clone the GitLab repository :
- Using tests from RTEMS Packages in SIS : Once RTEMS Packages are built, tests can be found at :
- In Legacy Networking :
rtems-net-legacy/build/sparc-rtems7-leon3/testsuites/<test-name>/<test>.exe - In Legacy Networking Demos :
rtems-net-legacy-demos/<test-name>/o-optimize/<test>.exe
[e.g. tests like ttcp, telnetd, etc.] - In Net Services :
rtems-net-services/buils/sparc-rtems7-leon3/<test>.exe - In lwIP :
rtems-lwip/build/sparc-rtems7-leon3/<test>.exe
- In Legacy Networking :
Other than GSoC contributions to RTEMS :
Over this long period since the community bonding period till Midterm evaluation, I have made 2 Merge requests for contributions to RTEMS other than GSoC :
leon: Include leon.h to resolve undefined leon_r32_no_cache@ RTOS/RTEMS- This Merge Request is regarding including
leon.hinbsp.hatrtems/bsps/sparc/leon3/includeensures that the functionleon_r32_no_cache()is recognized. This prevents “undefined reference” errors forleon_r32_no_cache(). - Merge Request Link
- This Merge Request is regarding including
leon3: Use sreload@ Packages/Legacy Networking- This Merge Request is regarding implementing correct LEON3 timer scaler reload register access by replacing
scaler_reloadwith the propersreloadfield. - Merge Request Link
- This Merge Request is regarding implementing correct LEON3 timer scaler reload register access by replacing
 Blogs during GSoC-2025 period at RTEMS for the project - Providing SPARC GRETH Network Drivers for lwIP
Blogs during GSoC-2025 period at RTEMS for the project - Providing SPARC GRETH Network Drivers for lwIP